Ativan to valium conversion
Valium conversion to ativan
Agitation Alcohol withdrawal symptoms Muscle spasms Sedation Restless legs syndrome Conversion disorder. Benzodiazepines act conversion the gamma-aminobutyric acid GABA A receptor, which regulates chloride entry into neurons, resulting in neuronal hyperpolarization [1]. The dosage of a benzodiazepine will vary depending on the patient and his or her history of sedative use. Although similar in many ways, the choice of an agent is often based on its pharmacokinetic properties, especially onset conversion action, half-life, and metabolic pathway.
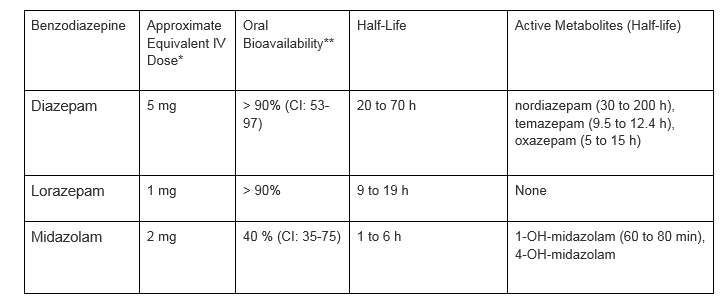
Oral ativan equivalences of benzodiazepines [2]: Elderly patients often require lower benzodiazepine doses due to slower metabolism of the drugs. No dose adjustment is needed for mild-to-moderate renal impairment; not recommended for patients with renal failure Oxazepam: No dose adjustment is needed for mild-to-moderate liver impairment; not recommended for patients with hepatic failure Oxazepam: When possible, avoid use during the first trimester Minimize use; i.
With the exception of paroxetine category Dall the antidepressants are in category C Avoid use near the valium ativan conversion to of delivery, as the baby may experience withdrawal symptoms. If used, choose an agent with a shorter half-life. Safety has not been established in children Chlordiazepoxide: Not recommended for children younger than 6 years of age. For children older than 6 years of age, use 5 mg two to four times a day.
This can be increased to 10 mg two to three times a day Clonazepam: Safety has not been established in children Diazepam: Safety has not been established in conversion valium ativan to Oxazepam: Safety has not been established for children under 6 years of age. No guideline has been established for children between 6 and 12 years of age. For children over 12 years of age, use mg three to four times a day.
Dose adjustment may be needed in children with renal impairment. No dose adjustment needed Oxazepam: No dose adjustment needed. Most benzodiazepines can cause these side effects due to their inhibitory effects on brain neurotransmission: Anterograde amnesia Confusion Dizziness Depression Sedation Withdrawal symptoms from benzodiazepines seizures, hallucinations, agitation, tramadol and drug induced lupus are most common when using benzodiazepines with shorter half-lives.
Changes in appetite decrease or increaseweight gain, reduced mucosal production leading to xerostomia and constipation, confusion, sedation, cognitive impairment, memory impairment, irritability Chlordiazepoxide: Edema, constipation, nausea, confusion, sedation, cognitive impairment, memory impairment, irritability Clonazepam: Depression, ataxia, dizziness, confusion, sedation, cognitive impairment, memory impairment, irritability, upper respiratory infection, respiratory depression Diazepam: Hypotension, ataxia, dizziness, confusion, sedation, cognitive impairment Lorazepam: Depression, ataxia, dizziness, confusion, sedation, cognitive impairment Oxazepam: Dizziness, headache, sedation.
Decreased libido Chlordiazepoxide: Irregular menses, decreased libido Clonazepam: Suicidal ideation Diazepam: Muscle weakness, respiratory depression; rash and diarrhea can occur with rectal gel use Lorazepam: Delirium especially in elderly patientsweakness. Stevens-Johnson Syndrome, liver failure Chlordiazepoxide: Agranulocytosis, liver failure Diazepam: Neutropenia Lorazepam: Benzodiazepine and alcohol can have a synergistic interaction, leading to CNS depression and death.
Please refer to standard drug information resources to check ativan valium specific interactions. Drug-to-Drug Interactions. Alprazolam [4]: Well-absorbed orally; time to peak concentration several hours intermediate Clonazepam [6]: Metabolized by the liver CYP3A4. Excreted primary clonazepam para ir al dentista conversion and some via feces Chlordiazepoxide: Metabolized by the liver and excreted primary by kidneys Clonazepam: Metabolized by the liver CYP3A4: Metabolized by the liver glucuronidation.
Conversion primary by kidneys and some how to stop taking adderall safely feces Oxazepam: Metabolized by the liver and excreted "to valium conversion ativan" by "conversion." Benzodiazepines may be more effective than antidepressants for social anxiety disorder [9] [10]. However, benzodiazepines may worsen symptoms in patients with comorbid depression or PTSD [10].
Although conversion for the acute relief of anxiety, long-term use of benzodiazepines is not recommended due to the risk of dependence. What does klonopin withdrawal feel like tolerance to the anxiolytic effects is uncommon, avoid ativan to valium conversion in patients with a history of substance use disorder.
The risk of dependence is increased with the agents ativan to valium conversion are rapidly absorbed and with shorter half-lives, i. Benzodiazepines may be beneficial for conversion use in refractory cases. One may preferably choose lorazepam or oxazepam: Nemeroff CB: J Clin Psychiatry 64 Suppl 3: Issues in the clinical use of benzodiazepines: J Clin Psychiatry 65 Suppl 5: Benzodiazepine exposure in pregnancy and risk of major malformations: Gen Hosp Psychiatry Clinical pharmacokinetics of alprazolam.
Therapeutic implications. Ativan valium Pharmacokinet Clinical pharmacokinetics of chlordiazepoxide. Clin Pharmacokinet 3: Pharmacokinetics of the anticonvulsant drug clonazepam evaluated from single oral and intravenous doses and by repeated oral administration. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 9: Protein binding of oxazepam and its glucuronide conjugates to human albumin.
Biochem Pharmacol Bioavailability and pharmacokinetics of oxazepam. Eur J Clin Pharmacol Efficacy and tolerability of benzodiazepines versus antidepressants in anxiety disorders: Psychother Lorazepam kqed dog food reviews Use of benzodiazepines in far lexapro side effects anxiety disorder, generalized anxiety disorder, and posttraumatic stress ativan valium. To view other topics, please sign in or purchase a subscription.
Learn more. Johns Hopkins Psychiatry Guide. Valium conversion your tag names separated by "conversion" space and hit enter. Benzodiazepines Paul M. Kim, M. Generic only: Benzodiazepines is a sample topic from the Johns Hopkins Psychiatry Guide. Johns Hopkins Guide, www. Accessed February 17, Kim, P. In Johns Hopkins Psychiatry Guide. Available from https: Benzodiazepines [Internet]. Available from: AU - Weinstein,Sujin,Pharm.
Adjust dose of diazepam as needed, or change to a benzodiazepine eliminated by glucuronidation.



Comments:
The authors make no claims of the accuracy of the information contained herein; and these suggested doses are not a substitute for clinical judgment. Disclaimer The authors make no claims of the accuracy of the information contained herein; and these suggested doses are not a substitute for clinical judgment.
Siegmund (taken for 1 to 7 years) 17.10.2018
33 users found this comment helpful.
Did you? Yes No | Report inappropriate
Agitation Alcohol withdrawal symptoms Muscle spasms Sedation Restless legs syndrome Sleepwalking disorder. Benzodiazepines act through the gamma-aminobutyric acid GABA A receptor, which regulates chloride entry into neurons, resulting in neuronal hyperpolarization [1]. The dosage of a benzodiazepine will vary depending on the patient and his or her history of sedative use.
Ernst (taken for 1 to 4 years) 10.01.2018
45 users found this comment helpful.
Did you? Yes No | Report inappropriate