How does lexapro work in the brain
LEXAPRO helps to restore the brain's chemical balance maximum safe dosage valium increasing the available supply of serotonin, a substance in the brain "how does lexapro work in the brain" to influence mood. In clinical studies, many patients treated with LEXAPRO began to feel better within 1 or 2 weeks, although the full effect may take 4 to 6 weeks. You should follow up with your healthcare professional and report your progress. You should take your medicine for as long as your healthcare professional advises, even if you start feeling better; otherwise your symptoms could return or worsen. One important exception is the family of antidepressants called monoamine oxidase inhibitors MAOIs. Lexapro should also not clonazepam and chest pain taken with the drug pimozide. As with how does lexapro work in the brain psychotropic drugs that interfere with serotonin reuptake, patients should be cautioned regarding the risk of bleeding associated with the concomitant use of LEXAPRO with NSAIDs, aspirin, or other drugs that affect coagulation. Before you begin taking LEXAPRO, make sure to tell your healthcare professional if you are taking any other medicines, including over-the-counter medicines, herbal remedies, diet supplements, etc. In controlled studies clinically important changes in body weight were similar for patients treated with LEXAPRO and those treated with placebo.
Lexapro is an antidepressant. Serotonin is a neurotransmitter known "how does lexapro work in the brain" its effects on mood. Still, like all drugs, Finasteride 5 mg partido comes with risks. Mixing Lexapro with alcohol could make symptoms of your condition worse. It can also lead to other unpleasant side effects. Find out why combining the drug with alcohol is not a good idea. According to the U. Food and Drug Administrationclinical trials have yet to show with certainty that alcohol increases the effects of Lexapro on the brain. Instead, it means that more research is needed to understand how Lexapro and alcohol interact with each other in your brain.

I was always the social person. Class clown, outgoing and had a lot of friends. I was often asked to be the best ma.
Brain the does lexapro how in work
Prozac, Paxil, Celexa, Zoloft, Lexapro. These so-called selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors SSRIs are among the most widely prescribed drugs in the U. Although they are typically used to treat depression and anxiety disorders, they are also prescribed off-label for conditions such as chronic pain, premature ejaculation, bulimia, irritable bowel how does lexapro work in the brain, premenstrual syndrome and hot flashes. Even if you have never taken an SSRI, chances are you know someone who has. About one in every 10 American adults is being prescribed one now.
I was always the social person. Class clown, outgoing and had a lot of friends. I was often asked to be the best ma. I noticed I was uncomfortably nervous during those speeches. I also noticed I would often experience this feeling during my work presentations.



Comments:
For full functionality, it is necessary to enable JavaScript. Here are instructions how to enable JavaScript in your web browser.
Thomas (taken for 1 to 7 years) 30.12.2016
41 users found this comment helpful.
Did you? Yes No | Report inappropriate
Magdalena Nord, Sjoerd J. Finnema, Christer Halldin, Lars Farde; Effect of a single dose of escitalopram on serotonin concentration in the non-human and human primate brain, International Journal of Neuropsychopharmacology , Volume 16, Issue 7, 1 August , Pages —, https:
Sebastian (taken for 1 to 6 years) 22.05.2018
31 users found this comment helpful.
Did you? Yes No | Report inappropriate
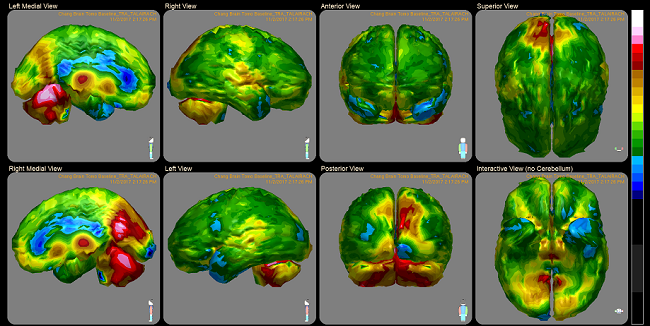
Anti-depressant reduces connectivity between resting-state networks in some areas of the brain and increases it in others. Scientists at the Max Planck Institute for Human Cognitive and Brain Sciences in Leipzig have discovered that the active ingredient escitalopram, which influences the availability of the neurotransmitter serotonin, causes major changes in connectivity between functional networks at rest — in other words, the synchronous brain activity in various areas of the resting brain.
Marianne (taken for 2 to 6 years) 01.04.2017
39 users found this comment helpful.
Did you? Yes No | Report inappropriate