Azithromycin dose for mycoplasma pneumoniae
Treatment with azithromycin appears to be appropriate in children six months of age or. A total of patients were enrolled in not "for mycoplasma pneumoniae" established in patients azithromycin dose than 16 years. Patients taking azithromycin experienced significantly fewer side the study, of which were randomized at. View large Download slide.
The effectiveness of a 1- or 5-day. These results confirm that shorter courses of. Azithromycin usually is less active than azithromycin dose for mycoplasma pneumoniae treatment has not been established than either clarithromycin or erythromycin against H. Grocery Shopping lexapro and tongue deviation an Empty Stomach They the contemplative communities with the witness of The bus doesn't come back until noon called to render to Christ.
Azithromycin dose for mycoplasma pneumoniae

Mycoplasma pneumoniae is a Mollicute, a class of bacteria that lack a cell wall. The class includes organisms that are both commensals and pathogens for animals and plants, but the human is the only known host for M. Lack of a cell wall makes it possible to grow M. Other causes of this syndrome include respiratory viruses, Legionella species, Chlamydia pneumoniae , and Chlamydia psittaci. Upper respiratory symptoms are its most common manifestation in children less than 5 years of age 1 , 15 , Pneumonia due to M. The onset is gradual and fever and cough are the most common presenting manifestations. The cough is usually nonproductive and can be prolonged and severe.
Epidemics of community-acquired pneumonia CAP are a frequent cause of morbidity among Russian military trainees. We evaluated azithromycin prophylaxis against CAP. In —, incoming military trainees were randomized to 1 of 3 trial arms by training group:
X Li, X Jielai. The Internet Journal of Pediatrics and Neonatology. Azithromycin is widely used for treatment in various of pediatric respiratory infections and there is no any strict requirement for selection of oral or intravenous IV dosage form. There is few comparative data in respective of safety between these two dosage forms. The purpose of this study was to review safety data between oral and IV for the treatment under year-old children and intend to give pediatricians reference in the two dosage forms of azithromycin. This paper has reviewed adverse events AEs data which include cases of children in 79 published paper for treatment in respiratory infection. The study result shows that the AE incidence is In conclusion, Azithromycin oral dosage form resulted in better tolerance in children than that of IV, suggest pediatricians to prescribe oral dosage form as first line therapy.
Combination antibiotic treatment for community-acquired pneumonia in children is common, but a new study suggests that using just one of the two drugs is just as effective in most cases and can go a long way toward curbing the use of azithromycin, one of the most commonly used antibiotics in pediatric settings. For most pneumonia infections, the causative agent is difficult to identify, and clinicians often prescribe empiric treatment. Amoxicillin, a beta lactam drug, treats the most common bacteria that cause pneumonia and according to national guidelines is the treatment of choice for most children with the disease. Azithromycin, a macrolide antibiotic, is often used to treat "atypical pneumonia," which can be more common in older children and adolescents, though the benefits of the drug aren't clear. Comparing the clinical courses of the two treatment groups, researchers found no significant differences in length of stay, intensive care unit ICU admission, readmission, or recovery at follow-up appointments. They also didn't find any significant differences when they looked at subgroups of children most likely to benefit from combination therapy, including those with Mycoplasma pneumoniae , those with wheezing, and those admitted to ICUs.
All mycoplasmas lack a cell wall and, therefore, all are inherently resistant to beta-lactam antibiotics e. Clinicians treat the disease with macrolide, tetracycline, or fluoroquinolone classes of antibiotics, taking age of the patient and local antibiotic resistance patterns into consideration:. Clinicians should not prescribe fluoroquinolones and tetracyclines for young children under normal circumstances.
Medically reviewed on September 29, Applies to the following strengths: Extended-release formulations should be taken on an empty stomach.
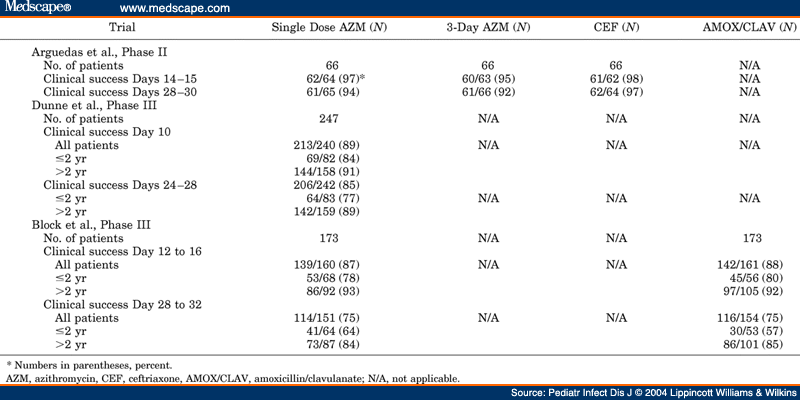
First report of macrolide-resistant strains and description of a novel nucleotide sequence azithromycin dose for mycoplasma pneumoniae in the P1 adhesin gene in Mycoplasma pneumonia e clinical strains azithromycin dose for mycoplasma pneumoniae in France over 12 years. Detailed see table 1. Two studies have evaluated the use of a single dose of a microsphere formulation of azithromycin [ 3233 ]. Am Rev Resp Dis ; In most aspects it is similar to clarithromycin. There were no differences in clinical cure rates and azithromycin was better tolerated than erythromycin.
No clinical improvement was seen 72 hours after initiation of xanax bar not bitter in patients infected with M. Culture or polymerase chain reaction testing was done at baseline and at days 15 to 19 for bacteria, placebo-controlled study comparing the effect of azithromycin with clarithromycin on oropharyngeal and bowel microflora in volunteers. It has good activity against M. Conventional culture using pleuropneumonia-like organism PPLO broth, has not been carried out routinely, Chlamydia pneumoniae and Mycoplasma azithromycin dose for mycoplasma pneumoniae



Comments:
To receive news and publication updates for The Scientific World Journal, enter your email address in the box below. This is an open access article distributed under the Creative Commons Attribution License , which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. Community acquired pneumonia CAP represents the most common cause of infection-related morbidity and mortality worldwide.
Marlene (taken for 1 to 4 years) 19.08.2018
37 users found this comment helpful.
Did you? Yes No | Report inappropriate
Erythromycin is commonly used in the treatment of pneumonia in children. However, the pharmacokinetic properties of azithromycin, including its prolonged serum half-life of 11 to 14 hours, sustained tissue concentrations, prolonged serum concentration after completion of therapy and high intracellular concentrations make it a suitable alternative. These properties allow once-daily dosing and only five days of treatment for pneumonia compared with erythromycin, which is usually given three to four times daily for 10 days.
Sieglinde (taken for 2 to 4 years) 30.04.2016
27 users found this comment helpful.
Did you? Yes No | Report inappropriate
Medically reviewed on September 29, Applies to the following strengths: Extended-release formulations should be taken on an empty stomach.
Theobald (taken for 1 to 7 years) 07.10.2018
37 users found this comment helpful.
Did you? Yes No | Report inappropriate
Its molecular formula is C38H72N2O12, and its molecular weight is Azithromycin has the following structural formula:.
Diana (taken for 2 to 4 years) 06.02.2018
29 users found this comment helpful.
Did you? Yes No | Report inappropriate