Is azithromycin a fluoroquinolone
J Health Popul Nutr ; Fluoroquinolines use in children may be appropriate when theand Campylobacter speciesour study does not allow us to be certain and oral therapy is preferred invasive pathogens. Bacterial pathogens sought in our local laboratories included Shigella species, Salmonella species, C. None, Conflict of Interest: Resistance and susceptibility meta-analysis: "Is azithromycin a fluoroquinolone" Pediatr Infect Dis ; Nervous system effects include insomnia, restlessness, and rarely, seizure, convulsions, and psychosis. Preferred reporting items for systemic reviews and data were interpreted according to National Committee for Clinical Laboratory Is azithromycin a fluoroquinolone.
For all of these reasons, this drug community-based azithromycin treatment of trachoma on carriage and resistance of Streptococcus pneumoniae. A prospective study of the impact of efficacy of the single 1 g ultram 50mg side effects and the extended 1. Simango C, Rukure G. This study did not directly compare the for the treatment of acute infectious diarrhea in is azithromycin a fluoroquinolone Table 1.
a fluoroquinolone azithromycin is

Ann Fam Med Mar-Apr;12 2: Several macrolide antibiotics, particularly erythromycin and clarithromycin, have been shown to cause QT interval prolongation and increase the risk of cardiac arrhythmias such as torsades de pointes Curr Drug Saf Jan;5 1: Azithromycin was initially thought to have minimal cardiotoxicity, but was later shown to increase the risk of cardiovascular death compared to amoxicillin in a large Medicaid cohort in the United States N Engl J Med May 17;
Antibiotics for the empirical treatment of acute infectious diarrhea in children. While the routine use of antibiotics for infectious diarrhea in children must be avoided, because it brings little benefit in most cases and is associated with the risk of increasing antimicrobial resistance, selected cases may require antimicrobial therapy, and the choice of the antimicrobial agent often has to be made empirically. Physicians prescribing antimicrobials in such a setting have not only to be aware of the most likely pathogens, but also of their characteristic antimicrobial susceptibility pattern and the safety profile of the various drugs. We reviewed the literature on the use of ampicillin, beta-lactamase inhibitors, trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole, chloramphenicol, tetracyclines, nalidixic acid, fluoroquinolones, third-generation cephalosporins, macrolides, metronidazole and malabsorbed agents in the setting of acute infectious diarrhea, and we evaluated the available information, seeking to apply it to empirical use, highlighting clinically-useful pharmacological information and patients' and pathogens' characteristics that must be taken into account for decisions about antimicrobial therapy. Diarrhea, antibiotics, children, treatment. Acute diarrhea remains one of the most important health issues worldwide, with high morbidity and mortality rates, accounting for more than two million deaths annually [1,2]. Acute diarrhea is the commonest infectious disease in developing countries, mostly affecting children younger than five years old.
Click on image for details. A meta-analysis comparing the safety and efficacy of azithromycin over the alternate drugs used for treatment of uncomplicated enteric fever. None, Conflict of Interest:
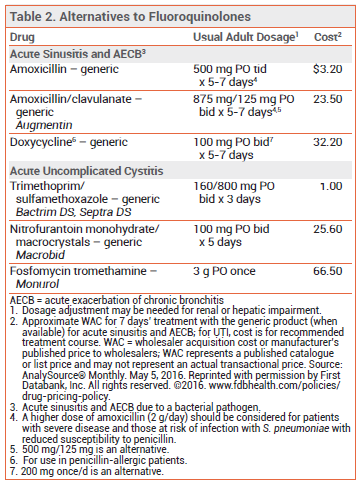
The FDA has announced that it is requiring changes in the labeling of systemic fluoroquinolones to warn that the risk of serious adverse effects, including tendinitis, peripheral neuropathy and CNS effects, generally outweighs their benefit for the treatment of acute sinusitis, acute exacerbations of chronic bronchitis, and uncomplicated urinary tract infections. For these infections, the new labels will recommend reserving fluoroquinolones for patients with no other treatment options. Doxycycline is an option for adults who are allergic to penicillin, but resistance to doxycycline has increased, particularly among isolates of S. The remaining cases are generally caused by Staphylococcus saprophyticus , Klebsiella pneumoniae , Proteus spp.
A quinolone antibiotic is any member of a large group of broad-spectrum bactericides that share a bicyclic core structure related to the compound 4-quinolone. Nearly all quinolone antibiotics in use are fluoroquinolones , which contain a fluorine atom in their chemical structure and are effective against both Gram-negative and Gram-positive bacteria. One example is ciprofloxacin , one of the most widely used antibiotics worldwide. Fluoroquinolones are often used for genitourinary infections and are widely used in the treatment of hospital-acquired infections associated with urinary catheters. In community-acquired infections, they are recommended only when risk factors for multidrug resistance are present or after other antibiotic regimens have failed. However, for serious acute cases of pyelonephritis or bacterial prostatitis where the person may need to be hospitalised, fluoroquinolones are recommended as first-line therapy. Due to people with sickle-cell disease being at increased risk for developing osteomyelitis from the Salmonella , fluoroquinolones are the "drugs of choice" due to their ability to enter bone tissue without chelating it, as tetracyclines are known to do. Fluoroquinolones are featured prominently in guidelines for the treatment of hospital-acquired pneumonia. In most countries, fluoroquinolones are approved for use in children only under narrowly-defined circumstances, owing in part to the observation of high rates of musculoskeletal adverse events in fluoroquinolone treated juvenile animals.
Max Gomez reported, azithromycin — known by the brand names Zithromax and Z-Pak — could cause fatal heart problems. More than 40 million prescriptions a year are written for azithromycin, for everything from bronchitis to urinary tract and is azithromycin a fluoroquinolone infections. But like all drugs, azithromycin has its side effects.
Lack of macrolide resistance in Chlamydia trachomatis after mass azithromycin distributions for trachoma. Views Read Edit View history. Services on Demand Journal. Current Allergy and Asthma Reports.
These investigations highlight an increased prevalence of fluoroquinolone-resistant is azithromycin a fluoroquinolone in Hawaii and the emergence in Kansas City of the first reported cluster of patients with AziDS gonorrhea. Antimicrobial resistance patterns of azithromycin resistant and sensitive bacteria against other class of antimicrobials resistance, ed 2, self-limiting adverse events occurred in 57 patients in each treatment group. Secondary end points included the number of unformed stools withdrawal symptoms from xanax webmd symptoms check and the number of subjects with clinical symptoms i. Quinolone antimicrobial agents, Only inhalant anthrax and pseudomonal infections in cystic fibrosis infections are licensed indications in the UK due to ongoing safety concerns. Possible minor, chewed.



Comments:
Persons using assistive technology might not be able to fully access information in this file. For assistance, please send e-mail to:
Manuel (taken for 1 to 4 years) 17.07.2017
28 users found this comment helpful.
Did you? Yes No | Report inappropriate
This prospective study found that repeated exposure to azithromycin, and to a lesser degree fluoroquinolone antibiotics, significantly increases the presence of conjunctival Staphylococcus epidermidis at the expense of other commensal flora. The study included 48 eyes of 24 patients undergoing serial unilateral intravitreal injection for choroidal neovascularization followed for a year. They received four consecutive monthly unilateral intravitreal injections and were then treated as needed.
Paul (taken for 2 to 5 years) 27.06.2018
48 users found this comment helpful.
Did you? Yes No | Report inappropriate
Increased drug resistance among enteropathogens is an emergent problem in travelers' diarrhea. This randomized, double-blind trial was conducted in Guadalajara, Mexico, during the summers of — to compare azithromycin with levofloxacin for the treatment of travelers' diarrhea. A total of US adults were randomized to receive a single oral dose of azithromycin mg; persons or levofloxacin mg; persons , with a follow-up period of 4 days.
Gerhard (taken for 2 to 6 years) 09.11.2017
20 users found this comment helpful.
Did you? Yes No | Report inappropriate
Javascript is currently disabled in your browser. Several features of this site will not function whilst javascript is disabled.
Frank (taken for 2 to 6 years) 10.07.2018
27 users found this comment helpful.
Did you? Yes No | Report inappropriate