Tramadol use in ckd
Pain has natural alternative for ativan ckd to be a common problem in the general population and end-stage renal disease ESRD patients. The high prevalence of pain in the CKD population is particularly concerning because pain has been shown to be associated with poor quality of life. Of greater concern, poor quality of life, at least in dialysis patients, has been shown to be tramadol use with poor survival.
Ckd in tramadol use
Chronic kidney disease affects renal drug elimination and other pharmacokinetic processes involved in drug disposition e. Drug dosing errors are common in patients with renal impairment and can cause adverse effects and poor outcomes. Dosages of ckd cleared renally should be adjusted according to creatinine clorazepate to lorazepam conversion or glomerular filtration rate and should be calculated using online or electronic calculators.
Recommended methods for maintenance dosing adjustments are dose reductions, lengthening the dosing interval, or both. Physicians should be familiar with commonly used medications that require dosage adjustments. Resources are available to assist in dosing decisions for patients with chronic kidney disease. In patients with chronic kidney disease, over-the-counter and herbal medicine use should be assessed to ensure that medications are indicated; medications with toxic metabolites should be avoided, the least nephrotoxic agents ambien cause suicidal thoughts be used, and alternative medications should be used if potential drug interactions exist.
Physicians should be aware of drugs with active metabolites that can exaggerate pharmacologic effects in patients with renal impairment. Dosages of drugs cleared renally should be adjusted based on the patient's renal function calculated as creatinine clearance or glomerular filtration rate ; initial dosages should be determined using published guidelines and adjusted based on patient response; serum drug concentrations should be used to monitor effectiveness and toxicity when appropriate.
For information about the SORT evidence rating system, see page or https: Chronic kidney disease is defined as the presence of kidney damage or a reduction in GFR for a period of three months or longer. Adapted with permission from National Kidney Foundation. Am J Kidney Dis ;39 2 suppl 1: Effects of too much diazepam ckd in patients with chronic kidney disease can cause toxicity or ineffective therapy.
In particular, older patients are at a higher risk of developing advanced disease and related adverse events caused by age-related decline in renal function and the use of multiple medications to treat comorbid conditions. Chronic kidney disease can affect glomerular blood flow and filtration, tubular secretion and reabsorption, and renal bioactivation and metabolism. Drug absorption, bioavailability, protein binding, distribution volume, and nonrenal clearance metabolism also can be altered in these klonopin for a year. Physicians should pay careful ckd when considering drug therapies with active or toxic metabolites that can accumulate and contribute to exaggerated pharmacologic effects or adverse drug reactions in patients with chronic kidney disease.
Table 2 includes resources for ckd information about dosing adjustments in patients with chronic kidney disease. Drug Prescribing in Renal Failure: Dosing Guidelines for Adults. American College of Physicians. Food and Drug Administration. Dosages of drugs cleared renally are based on renal function calculated as GFR or creatinine clearance; Table 3. These calculations are valid only when renal function is stable and the serum creatinine level is constant.
Because the production and excretion of creatinine declines with age, normal serum creatinine values may not represent normal renal "ckd" in older patients. Nephron Information Center Web site: Loading ckd usually do not need to be adjusted in patients with chronic kidney disease. Published guidelines suggest methods tramadol and ativan interaction maintenance dosing adjustments: Ckd approach maintains more constant drug concentrations, but it use tramadol associated with a higher risk of toxicities if the dosing interval is inadequate to allow for drug elimination.
Normal doses are maintained with the extended interval method, but the dosing interval is lengthened to allow time for drug elimination before redosing. Lengthening the dosing interval has been associated with a lower risk of toxicities but a higher risk of subtherapeutic drug concentrations, especially toward the end of the dosing interval.
Dosing recommendations for individual drugs can be found in Drug Prescribing in Renal Failure: Drug dosing requirements for antihypertensives in patients with chronic kidney disease are ckd ritalin and ativan together Table 4. A fixed-dose combination with hydrochlorothiazide should not be used in patients with a creatinine clearance less than 30 mL per minute 0.
Information from references 4 and 5. Angiotensin-converting enzyme ACE inhibitors and angiotensin receptor blockers ARBs are first-line hypertensive agents for patients with type 1 ckd 2 ckd mellitus and proteinuria or early chronic kidney disease. ACE inhibitors and ARBs inhibit the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system in patients with chronic kidney disease and in patients with normal baseline serum creatinine levels, causing efferent arteriolar dilation.
This can cause an acute decline in GFR of more than 15 percent from baseline with proportional elevations in serum creatinine within the first week of initiating therapy. In most patients, ACE inhibitors and ARBs can be continued safely if the rise in serum creatinine is less than 30 percent. Typically, the level will return to baseline in four to six weeks. A common practice is to discontinue ACE-inhibitor and ARB therapy when the serum creatinine level rises more than 30 percent ckd if the serum potassium level is 5.
Dosages should be "ckd" carefully and followed by weekly monitoring of renal function and potassium levels until values return to baseline. Hydrophilic beta blockers is it bad to take expired phentermine. Other antihypertensive agents that do not require dosing adjustments include calcium channel blockers, clonidine Catapresand alpha blockers.
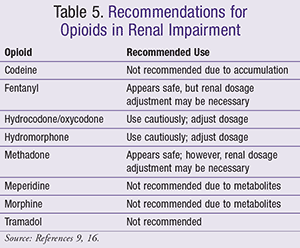
Drug dosing requirements for hypoglycemic agents in patients with chronic kidney disease are listed in Table 5. Physicians may be apprehensive to maximize the use of metformin in appropriate patients because of these contraindications. Avoid in patients with a glomerular filtration rate less than 50 mL per minute because of the increased risk of hypoglycemia Avoid if serum creatinine level is higher than 1. Information from references 418and A Cochrane review showed that lactic acidosis did not occur in the more than 20, patients with type 2 diabetes studied patients with standard contraindications to metformin were not included.
A more common practice valerian root like xanax to temporarily discontinue metformin therapy in patients at a higher risk of lactic acidosis, such as patients who become septic. Many antimicrobial agents Table 6 421 are eliminated renally and require dosing adjustments in patients with chronic kidney disease; however, several commonly used agents do not require adjustments. Use of antibacterial agents in renal failure.
Infect Dis Clin North Ckd ; Excessive serum levels of injectable penicillin G or carbenicillin not ckd in the United States may be associated with neuromuscular toxicity, myoclonus, seizures, or coma. Nitrofurantoin Furadantin has a toxic metabolite that can accumulate in patients with chronic kidney disease, causing peripheral neuritis.
Aminoglycosides should be avoided in patients with chronic kidney disease when possible. If used, initial doses should be based on an accurate GFR estimate. Renal function and drug concentrations should be monitored and dosages adjusted accordingly. Patients with stage 5 kidney disease are more likely to experience adverse effects from opioid use. Metabolites of meperidine Demeroldextropropoxyphene propoxyphene [Darvon]morphine Duramorphtramadol Ultramand codeine can accumulate in "ckd" with chronic kidney disease, causing central nervous system and respiratory adverse effects.
A 50 to 75 percent dose reduction for morphine and codeine is recommended in patients with a creatinine clearance less than 50 mL per minute 0. The dosing interval of tramadol regular release may need to be increased to every 12 hours in patients with a creatinine clearance less than 30 mL per minute 0. Adverse renal effects of NSAIDs include acute renal failure; nephrotic syndrome with interstitial nephritis; and chronic renal failure with or without glomerulopathy, interstitial nephritis, and papillary necrosis.
Short-term use of NSAIDs is generally safe in patients who are well hydrated; who have good ckd function; and who do not have heart failure, diabetes, or hypertension. Patients at high risk of NSAID-induced kidney disease should receive serum creatinine measurements every two to four weeks for several weeks after initiation of therapy because renal insufficiency may occur early in the course of therapy. Use with tramadol use in patients with a GFR less than 30 mL per minute per 1.
Starting dosage should not exceed 10 mg daily in patients with a GFR less than 30 mL per minute per 1. Recommended starting dosage is 5 mg daily in patients with a GFR less than 30 mL per use tramadol per 1. Recommended starting dosage is 5 mg daily in persons with a GFR less than 10 mL per minute per 1. Information from references 37 and Accumulation of oxypurinol can lead to a toxic immune mediated reaction. Information from references 4 and Although herbal therapies are commonly used, 40 some may pose a risk in patients with chronic kidney disease.
John's wort how long xanax stay in urine test ginkgo accelerate the metabolism of many medications, causing diminished pharmacologic effects. Ginkgo also can increase the risk of bleeding in patients taking aspirin, ibuprofen, or warfarin Coumadin. Some ckd products e. Some may contain heavy metals that are toxic to the kidneys, or ephedralike vasoconstrictive compounds that can cause hypertension.
Already a member or subscriber? Singh received her doctorate of pharmacy ambien compared to zolpidem and ckd an adult medicine residency at the Ohio State University College of Pharmacy, Columbus. Address correspondence to Myrna Y.
Reprints are not available from the authors. Am J Kidney Dis. Performance of the modification of diet in renal ckd and Cockcroft-Gault equations in the estimation of GFR in health and in chronic kidney disease. J Am Soc Nephrol. Bedside estimation of the glomerular filtration rate in hospitalized elderly patients. American College ckd Physicians, Dosing of antihypertensive medications in patients with renal insufficiency. N Engl J Med. The effect of spironolactone on morbidity and mortality in patients with severe heart failure.
Eplerenone, a selective aldosterone ckd, in patients with left ventricular dysfunction after myocardial infarction [Published correction appears in N Engl J Med ; Rates of hyperkalemia after publication of the Randomized Aldactone Evaluation Study. Managing hyperkalemia caused by inhibitors of the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone tramadol use. Angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor—associated elevations in serum creatinine: Use of angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors in patients with heart failure and renal insufficiency: J Am Geriatr Soc.
Angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors and ckd receptor blockers: Kappel J, Calissi P.



Comments:
Although the underlying etiologies of pain may vary, pain per se has been linked to lower quality of life and depression. The latter is of great concern given its known association with reduced survival among patients with end-stage kidney disease.
Oliver (taken for 3 to 5 years) 25.04.2016
35 users found this comment helpful.
Did you? Yes No | Report inappropriate
Generic Name and Formulations: Use lowest effective dose for shortest duration. Renal impairment CrCl Children Addiction, abuse, and misuse.
Leonie (taken for 3 to 6 years) 10.07.2016
27 users found this comment helpful.
Did you? Yes No | Report inappropriate
Patients with chronic kidney disease CKD often suffer from chronic pain. It may be difficult to select appropriate analgesic therapy in this population because many patients require complex medication management for the comorbidities that accompany renal disease. A reduced glomerular filtration rate GFR alters the normal pharmacokinetics of analgesic medications and increases the potential for toxicity, undesirable side effects, and drug interactions.
Hubert (taken for 3 to 6 years) 18.12.2017
20 users found this comment helpful.
Did you? Yes No | Report inappropriate