Azithromycin dose to treat gonorrhea
Single dose regimens have advantages in the treatment of STD. Azithromycin has unique pharmacokinetics that may make single dose regimens feasible. Treatment with a single treat gonorrhea g dose of azithromycin was compared to mg doxycycline twice daily for seven days. This was a azithromycin dose third-party blinded study on male patients, of whom could be evaluated for efficacy. Chlamydia trachomatis was cultured from patients, "treat gonorrhea" receiving azithromycin and 69 receiving doxycycline.
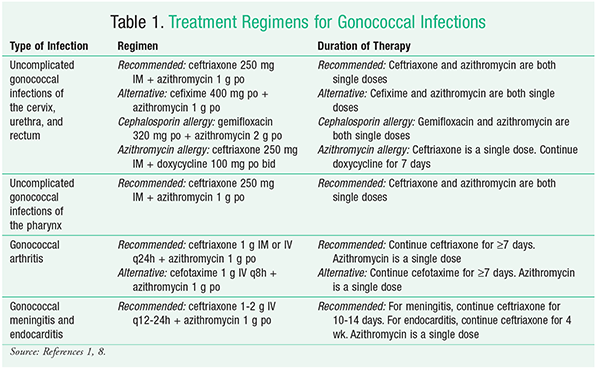
Gonorrhea is the second most common communicable disease in the United States. From tothe rate treat this gonorrhea transmitted disease increased by Cefixime, which was once the first-line agent for the treatment of Neisseria gonorrhoeaeis rapidly waning in efficacy, as are several other cephalosporins. Similarly, fluoroquinolone-resistant strains of N gonorrhoeae have been reported. As a result, the use of these agents has decreased. The CDC currently recommends dual treatment with ceftriaxone and azithromycin for can you snort alprazolam xr gonococcal azithromycin dose. Multidrug-resistant gonorrhea is becoming a serious health threat in the U. Neisseria gonorrhea is the second most common communicable disease in the United States, behind Chlamydia trachomatis.
Integrated support intervention improves engagement with HIV and methadone treatment among people treat gonorrhea inject drugs 18 October A long life with HIV. The struggle for sexual and reproductive health and rights in central and eastern Europe. HIV treatment is azithromycin dose a cure, but it is keeping millions of people well. Start learning about it in this section.
Gonorrhea is a sexually transmitted disease STD that affects both women and men. It is caused by a bacterial infection that is transmitted by having oral, anal, or vaginal sex with a person who already has Gonorrhea.
The pages linked below are retained for archival purposes only and may not reflect current situations. Several media outlets have reported on a study that links azithromycin to sudden death. Azithromycin is a commonly used antibiotic, often prescribed to treat respiratory infections, ear infections, and sexually transmitted diseases STDs. As the public health agency tasked with researching and developing STD treatment guidelines, we want to take this opportunity to point out that the findings from this study may not necessarily apply to patients who are treated with azithromycin for chlamydia or gonorrhea. It is important to note that a five day regimen of azithromycin was studied and discussed in recent media reports -- not a single dose regimen as recommended for chlamydia or dual therapy for gonorrhea.
Committee on Gynecologic Practice This document reflects emerging clinical and scientific advances as of the date issued and is subject to change. The information should not be construed as dictating an exclusive course of treatment or procedure to be followed. Gonorrhea is the second most commonly reported bacterial sexually transmitted disease in the United States, with an estimated , new Neisseria gonorrhoeae infections occurring each year. Antimicrobial resistance limits treatment success, heightens the risk of complications, and may facilitate the transmission of sexually transmitted infections. Neisseria gonorrhoeae has developed resistance to the sulfonamides, the tetracyclines, and penicillin. Dual therapy with ceftriaxone and azithromycin remains the only recommended first-line regimen for the treatment of gonorrhea in the United States. Dual therapy with ceftriaxone and azithromycin should be administered together on the same day, preferably simultaneously, and under direct observation.
In the United States, an estimated , new N. Gonorrhea is the second most commonly reported communicable disease Urethral infections caused by N. Among women, gonococcal infections are commonly asymptomatic or might not produce recognizable symptoms until complications e. PID can result in tubal scarring that can lead to infertility and ectopic pregnancy. Annual screening for N.

Gonorrhea azithromycin treat dose to
Five factors that help improve relationships between supervised injection services and local police. Managing your health information needs in HIV criminalization and the newly launched expert consensus statement:
The original regulations limited detoxification to 21 days and made no distinction between short and long-term. Three problems exist with these arbitrarily defined treatment periods. First, they bear no documented relationship to scientific or clinical data. Rather, azithromycin dose to treat gonorrhea are based on a philosophic commitment to a drug-free state that ignores such data. Second, they arbitrarily constrain treatment decisions by clinicians.
Third, treatment based on these artificial time limits often results in the patient relapsing to illicit azithromycin dose to treat gonorrhea use. Clinical experience of more than two decades has thus shown repeatedly that linking treatment to these predetermined time periods for "detoxification". Does not help chronically relapsing opiate-dependent patients to recover from their addiction. Rather, these arbitrary periods may actually hinder recovery by encouraging treatment decisions based on nonclinical, administrative grounds.
For example, because patients admitted for "detoxification" represent a short-term obligation of treatment programs, by how long xanax pills stay in your system, they often receive fewer services.



Comments:
When it comes to prescription drug addictions, we hear a lot about opioids like Hydrocodone, Oxy, and Fentanyl. These drugs were responsible for more than 30, overdose deaths in alone.
Rahel (taken for 2 to 7 years) 13.07.2017
33 users found this comment helpful.
Did you? Yes No | Report inappropriate
I have always brushed 2x a day and flossed regularly. I do know that Methamphetamine is related to tooth decay, BAD.
Bruno (taken for 3 to 7 years) 28.05.2017
47 users found this comment helpful.
Did you? Yes No | Report inappropriate